- Databricks
- December 12, 2022
Databricks Medallion Architecture: Distill your data to do more

- Databricks
- December 12, 2022
Databricks Medallion Architecture: Distill your data to do more
Data is the most precious resource for a business to examine and view insights for better decision-making. However, enormous data flow makes data processing and analyzing arduous for business owners. One of the reason why enterprises are exploring outside the conventional data architecture to meet their data processing and analytical needs.
Databricks hopes to solve this problem using Medallion Architecture and Delta Lake Framework in Lakehouse. This Architecture promises ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability) by percolating data through various levels of conversions and validations before storing it in a format intended for analysis.
Although cloud computing presents a lot of opportunities for growth for any enterprise, there are many factors that can become a challenge to a seamless flow. These are some of the common hindrances that need to be addressed to leverage the cloud to optimum.
- Lack of transactional support
- Inconsistent data quality
- Complication in addition, subtraction and modification of date in the lake
- Data governance results in data swamps instead of lake
- Complex data model may present difficulties in ingestion and implementation.
With the Medallion architecture, these obstructions can not only be overcome but also turn into opportunities for total enterprise evolution.
What is Medallion Architecture? And, what are its three layers?
Medallion architecture, also known as “multi-hop” architecture, is a data design pattern used to organize the data in a lakehouse, with the goal of incrementally and progressively elevating the data as it passes through each layer of the architecture (Bronze to Silver to Gold layer tables).
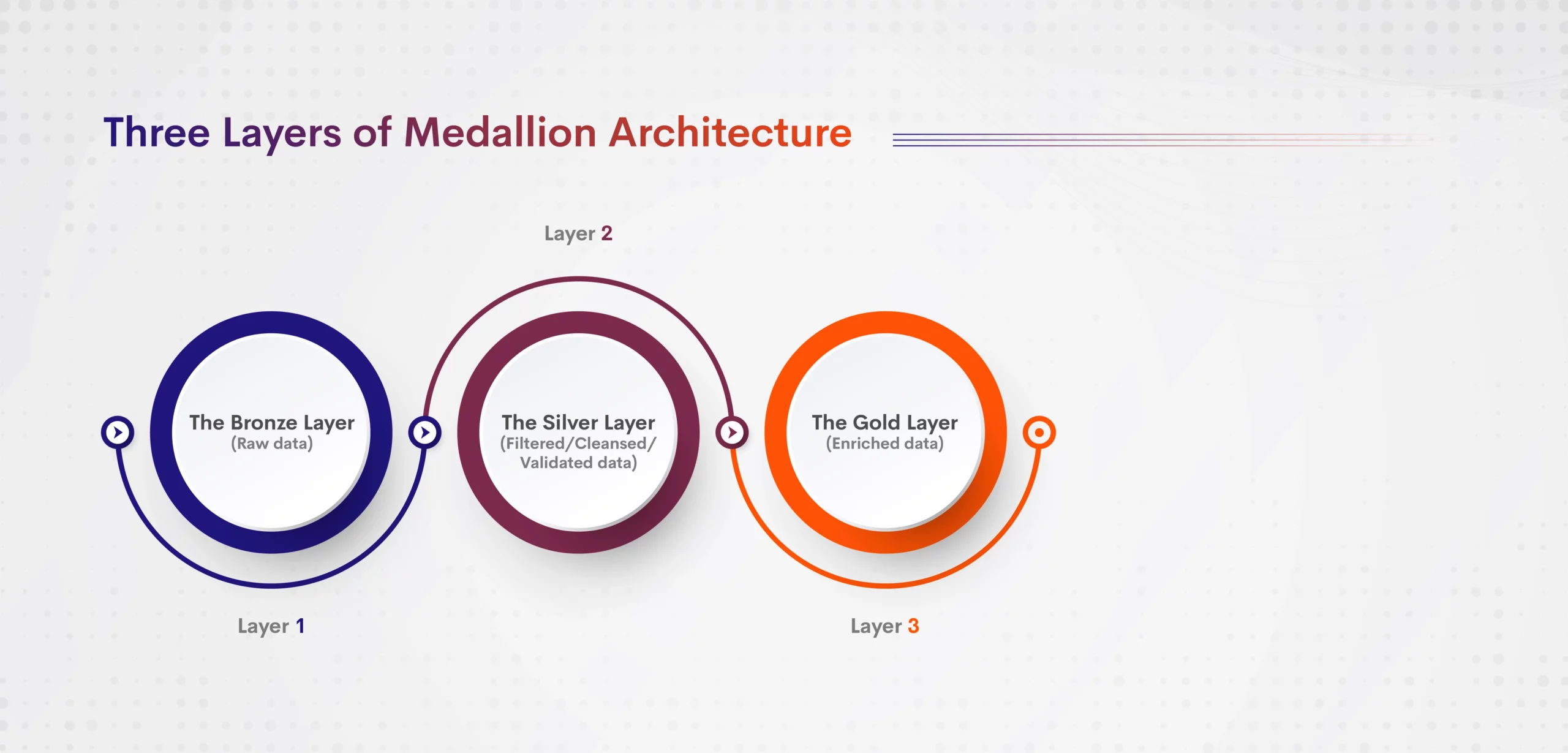
- The Bronze layer (Raw data) – This layer comprises the unprocessed or raw data (can be any blend of streaming and batch transactions) ingested from numerous data sources and preserves them as it is. The table structure in this layer is similar to that of the source system table structure with any supplementary metadata columns that hold the load date/time, file name, Load ID, etc.,
- The Silver layer (Filtered/Cleansed/Validated data) – Data is reclaimed from the bronze layer and added to the silver layer after being filtered, cleansed, trimmed, and run through other procedures to validate the data. In this layer, we apply business rubrics to transform the data into the preferred format. With the help of this layer, the data is transformed into an enterprise asset, empowering use cases like ad-hoc reporting, sophisticated analytics, and machine learning.
- The Gold layer (Enriched data) – Data is gathered in this layer from the silver layer, which is then primed and combined for business usage. Quality and business principles are applied to the said data to augment it into a format appropriate for analytics. Data and Business analysts rely highly on this layer to gauge insights from the data.
Benefits of a Lakehouse Architecture
Organizations generate data from innumerable sources like IoT devices, OnPrem source systems, and numerous databases, amassing them in a data lake for analytics and machine learning processes. To get the best of this data, modern architecture is a must, a solution is required that permits them to move data amid data lakes to store data efficiently. Lakehouse architecture is the perfect solution as it provides many benefits-
- Transactional support: Data pipelines would read or write data concurrently in an enterprise lakehouse. The ACID process guarantees consistency as many parties simultaneously read or write data, typically using SQL.
- Schema application and governance: It safeguards data quality by disregarding insufficient data which does not fulfill the schema defined for the table.
- BI support: It is highly compatible with BI tools and directly channelizes source data.
- Independent storage from computing: Separate storage and computes clusters necessitate fewer efforts to take scale to simultaneous users and data sizes.
- Open: It supports open standardization formats, such as Parquet, and they provide an API, so many tools and engines can efficiently access the data directly.
- Support for assorted data types ranging from unstructured to structured data: Including unstructured data like video, streaming data, etc.
- Supports data science, machine learning, SQL, and analytics.
As the data passes through the architectural layers of the lakehouse, the quality of data keeps getting better. Much akin to the distillation process, each layer generates processed data and its byproduct that can be used in many different ways by an enterprise.
As a databricks services partner, MSRcosmos offers you robust data processing techniques, framework, strategies, methodology, and road map to promptly deploy this lakehouse architecture. Get in touch with us to learn how you can start implementing this architecture efficiently and successfully to your business processes today.




